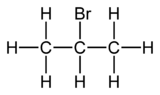
2-溴丙烷
外观
| 2-溴丙烷 | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
| |||
| |||
| IUPAC名 2-Bromopropane[1] | |||
| 别名 | 异丙基溴、对溴丙烷[2] | ||
| 识别 | |||
| CAS号 | 75-26-3 | ||
| PubChem | 6358 | ||
| ChemSpider | 6118 | ||
| SMILES |
| ||
| Beilstein | 741852 | ||
| UN编号 | 2344 | ||
| EINECS | 200-855-1 | ||
| RTECS | TX4111000 | ||
| MeSH | 2-bromopropane | ||
| 性质 | |||
| 化学式 | C3H7Br | ||
| 摩尔质量 | 122.99 g·mol−1 | ||
| 外观 | 无色液体 | ||
| 密度 | 1.32 g·cm−3(15 °C)[3] 1.31 g·cm−3(20 °C)[4] | ||
| 熔点 | −89 °C(184 K)[5] | ||
| 沸点 | 59.5 °C(332.6 K)[5] | ||
| 溶解性(水) | 3.2 g L−1 (at 20 °C) | ||
| log P | 2.136 | ||
| 蒸气压 | 32 kPa(20 °C) | ||
| kH | 1.0 μmol·Pa−1·mol−1 | ||
| 折光度n D |
1.4251(20 °C,589.3 nm)[4] | ||
| 黏度 | 0.4894 mPa·s(20 °C) | ||
| 热力学 | |||
| ΔfHm⦵298K | −129 kJ mol−1 | ||
| ΔcHm⦵ | −2.0537–−2.0501 MJ mol−1 | ||
| 热容 | 135.6 J K mol−1 | ||
| 危险性 | |||
GHS危险性符号 
| |||
| GHS提示词 | 危险 | ||
| H-术语 | H225, H360, H373 | ||
| P-术语 | P210, P308+313 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| 相关物质 | |||
| 相关化合物 | |||
| 若非注明,所有数据均出自标准状态(25 ℃,100 kPa)下。 | |||
2-溴丙烷是一种有机化合物,化学式为C3H7Br,是丙烷的亚甲基氢被溴取代的产物。它的同分异构体是1-溴丙烷。它在2023年被列入IARC第2A类致癌物质。[6]
制备
[编辑]异丙醇和溴化试剂(如硫酸-溴化钠[8]、磷-溴[9]、三溴化磷[10]等)发生溴化反应,也能得到2-溴丙烷。
反应
[编辑]2-溴丙烷可以用于合成异丙基化合物,例如在碳酸钾的存在下,2-溴丙烷和4-羟基苯甲醛在乙腈中反应,可以得到4-异丙氧基苯甲醛;[11]碳酸铯作为碱、四(三苯基膦)钯作为催化剂,它和呋喃-2-硼酸反应,得到2-异丙基呋喃[12]。
它可以和碘化钠在丙酮中发生卤素交换反应,生成2-碘丙烷;[13]它和硫氰酸钠发生类似反应,生成硫氰酸异丙酯。[14]它也可以和一氟化氯反应,生成2-氟丙烷。[15]
参考文献
[编辑]- ^ 2-bromopropane - Compound Summary. PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. Identification. 27 March 2005 [15 June 2012]. (原始内容存档于2013-12-14).
- ^ Wilfred L.F. Armarego and Christina Li Lin Chai, Purification of laboratory chemicals, 7th edition, Butterworth-Heinemann, 2013, p. 176 (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
- ^ Timmermans, J.; Martin, F. The work of the International Bureau of Physical-Chemical Standards. III. Study of the physical constants of twenty organic compounds. Journal de Chimie Physique et de Physico-Chimie Biologique, 1928. 25. 411-451. ISSN: 0021-7689.
- ^ 4.0 4.1 Afenkov, N. I. Measurement of the specific volumes of a few organic liquids with the help of the sectional dilatometer. Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Khimiya i Khimicheskaya Tekhnologiya, 1958. 6. 128-132. ISSN: 0579-2991.
- ^ 5.0 5.1 "PhysProp" data were obtained from Syracuse Research Corporation of Syracuse, New York (US). Retrieved from SciFinder. [2020-07-12]
- ^ IARC MONOGRAPHS ON THE IDENTIFICATION OF CARCINOGENIC HAZARDS TO HUMANS. WHO. 2023-12-01 [2023-12-06]. (原始内容存档于2021-04-05).
- ^ Griesbaum, Karl; Mach, Helmut. Crossover products from joint reactions of alkenes and alkynes with hydrogen halides. Chemische Berichte, 1982. 115 (12): 3818-3829. ISSN: 0009-2940.
- ^ 王玉凤, 王江. 2–溴丙烷合成的研究. 黑龙江日化, 1998, (4): 4-6.
- ^ Goshorn, R. H.; Boyd, Thomas; Degering, E. F. Alkyl and alkylene bromides. II. Phosphorus and bromine method. Organic Syntheses, 1941. 1 (2). 36-41. ISSN: 0078-6209.
- ^ Mundy, Bradford P.; Stewart, Catherine A. Phosphorus(III) bromide. e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, 2008. pp 1-4. ISBN 978-0-470-84289-8.
- ^ Treu, Matthias. Synthesis of Novel Galanthamine Analog Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors via Tandem Cyclization [Dissertation]. 2000. Vienna University of Technology.
- ^ Li, Jiuyi; Lu, Lin; Pan, Qi; Ren, Yanwei; Liu, Bo; Yin, Biaolin. Palladium-Catalyzed Dearomatizing Alkoxydiarylation of Furan Rings by Coupling with Arylboronic Acids: Access to Polysubstituted Oxabicyclic Compounds. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2017. 359 (11): 2001-2007. ISSN: 1615-4150. DOI: 10.1002/adsc.201601437.
- ^ Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition, Prentice Hall, 1989
- ^ Shriner, R. L. Isopropyl thiocyanate. Organic Syntheses, 1931. XI. 92-93. ISSN: 0078-6209. DOI: 10.15227/orgsyn.011.0092.
- ^ Morozova, T. V.; Chuvatkin, N. N.; Panteleeva, I. Yu.; Boguslavskaya, L. S. Reactions of chlorine monofluoride. IV. Relative rates of the substitutive fluorination of bromo-substituted alkanes. Hydride and other migrations during fluorination. Zhurnal Organicheskoi Khimii, 1984. 20 (7): 1379-1388. ISSN: 0514-7492.




