白颊犀鸟
| 白颊斑嘴犀鸟 | |
|---|---|

| |
| 雄性 | |
| 科学分类 | |
| 界: | 动物界 Animalia |
| 门: | 脊索动物门 Chordata |
| 纲: | 鸟纲 Aves |
| 目: | 犀鸟目 Bucerotiformes |
| 科: | 犀鸟科 Bucerotidae |
| 属: | 皱盔犀鸟属 Rhabdotorrhinus |
| 种: | 白颊斑嘴犀鸟 R. exarhatus
|
| 二名法 | |
| Rhabdotorrhinus exarhatus | |
| 亚种 | |
| |
| 异名 | |
| |
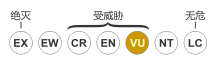
白颊犀鸟(学名:Rhabdotorrhinus exarhatus,英语:Sulawesi hornbill,台湾作白颊斑嘴犀鸟),是犀鸟目犀鸟科皱盔犀鸟属下的一种鸟类。[3]该物种仅分布于印度尼西亚的苏拉威西岛及其周围的小岛上,于通常海拔低于650公尺的原始低地森林内,是一种小型的黑色犀鸟。[3][4]虽然其族群数量仍未有估计,但因其低地森林的栖息地的开发速度相当严重,因此被列为易危物种。[1][5]
本物种是由法国鸟类学家康拉德·雅各·特明克于1823年发表,并命名为Buceros exarhatus。[3][6]在分类上,本物种原先被归于斑嘴犀鸟属下,但后来根据分析发现实际上应属于斑嘴犀鸟属的姊妹支群,因而与其他在棕颈犀鸟属中物种被立为现在的皱盔犀鸟属。[3][7]其属名Rhabdotorrhinus是由希腊语的rhabdotos(意即“条纹的”)及rhis(意即“犀牛”)组成。[8]:333种小名exarhatus则为拉丁语exaratus,是“耕种”或“犁地”的意思。[8]:154

指名亚种雄鸟的脸及喉部为白色(或被染成黄色):鸟喙呈淡黄色,上喙隆起部分呈褐色,下喙基部呈黑色;脸上的裸露皮肤接近肉色;而雌鸟体型较小,除了喙尖及下喙基部有淡奶油色的区域之外,几乎全身皆为黑色。[4]幼鸟与成年雄鸟相似但没有上喙隆起,大约至80日龄之后幼鸟才会开始发展出成鸟特征。[4]sanfordi亚种的差异在于其下喙基部的条纹为淡奶油色而非单纯黑色。[4]
这种鸟类主要为植食性,主要食用水果,并包含一些小型动物如无脊椎动物。[9][4]繁殖时会采取以2—10只的小队协同合作,通常雌鸟会将自己封在巢穴内,并由其他帮手负责喂养。[10][4]一个孵化周期约需70—90天;其中孵化需16—19天,喂养则需约55—70天,之后幼鸟就有离巢的能力。[10][4]其体长45公分,体重平均约370.0公克,鸟喙宽平均约25.2公釐、深平均约38.4公釐、嘴峰长平均约91.6公釐;翼长平均约226.8公釐;跗跖约42.3公釐;尾长约208.0公釐。[9][4]

在1985年至1997年期间,由于商业伐木、移民和种植园的扩张,苏拉威西岛的低地森林面积减少了89%。[11]而在2021年的研究显示该地的低地森林仍以近30%的速度消失。[5]因为白颊斑嘴犀鸟还有被作为食物或宠物饲养的可能,在面临栖地破碎化的情况下,它们因此被《国际自然保护联盟濒危物种红色名录》列为易危物种。[1][5]
参考资料
[编辑]- ^ 1.0 1.1 1.2 BirdLife International. Rhabdotorrhinus exarhatus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2022: e.T22682504A210091404. [2023-11-01]. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2022-1.RLTS.T22682504A210091404.en
 .
.
- ^ CITES. Appendices (PDF). Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora Main navigation. [2023-06-24]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2023-07-02) (英语).
- ^ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 International Ornithologists' Union. Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P. , 编. IOC World Bird List 13.2. 2023 [2023-09-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-09-09) (英语).
- ^ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 del Hoyo, Josep; Elliott, Andrew; Sargatal, Jordi (编). Handbook of the birds of the world
 6. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. 2001: 506-507 [2023-11-01]. ISBN 978-84-87334-30-6 (英语).
6. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. 2001: 506-507 [2023-11-01]. ISBN 978-84-87334-30-6 (英语).
- ^ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Berryman, A.; Derhé, M.; Holmes, D.; Kinnaird, M.; Lambert, F.; Mulyawati, D.; O'Brien, T.; Schutz, P.; Symes, A.; Westrip, J.R.S. Sulawesi Hornbill (Rhabdotorrhinus exarhatus) - BirdLife species factsheet. BirdLife Data Zone. [2023-11-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-23) (英语).
- ^ Temminck, C.J.; Buffon, Georges Louis Leclerc; Huet, Nicholas; Laugier de Chartrouse, Guillaume Michel Jerôme Meiffren; Prêtre, J. G. Nouveau recueil de planches coloriées d'oiseaux : pour servir de suite et de complément aux planches enluminées de Buffon, édition in-folio et in-4⁰ de l'Imprimerie royale, 1770. Chez Legras Imbert et Comp. 1838: 97–98 [2023-11-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-11-01) (法语).
- ^ Gonzalez, Juan-Carlos T.; Sheldon, Ben C.; Collar, Nigel J.; Tobias, Joseph A. A comprehensive molecular phylogeny for the hornbills (Aves: Bucerotidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 2013-05-01, 67 (2): 468–483 [2023-11-01]. ISSN 1055-7903. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2013.02.012. (原始内容存档于2023-11-01).
- ^ 8.0 8.1 Jobling, James A. The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. 2010. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4 (英语).
- ^ 9.0 9.1 Tobias, Joseph A.; Sheard, Catherine; Pigot, Alex L.; Devenish, Adam J. M.; Yang, Jingyi; et al. AVONET: morphological, ecological and geographical data for all birds. Ecology Letters. 2022-03, 25 (3): 581—597 [2023-07-22]. doi:10.1111/ele.13898. (原始内容存档于2023-02-03) (英语).
- ^ 10.0 10.1 O'Brien, Timothy G. Behavioural ecology of the North Sulawesi Tarictic Hornbill Penelopides exarhatus exarhatus during the breeding season. Ibis. 1997-01, 139 (1): 97–101 [2023-11-01]. ISSN 0019-1019. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919X.1997.tb04507.x. (原始内容存档于2023-11-01) (英语).
- ^ Winarni, Nurul L.; Jones, Martin. Effect of anthropogenic disturbance on the abundance and habitat occupancy of two endemic hornbill species in Buton island, Sulawesi. Bird Conservation International. 2012-06, 22 (2): 222–233 [2023-11-01]. ISSN 1474-0001. doi:10.1017/S0959270911000141. (原始内容存档于2022-05-03) (英语).