大星形十二面體
外观
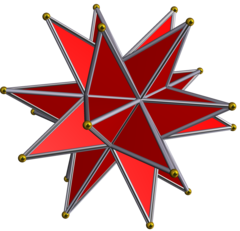 (按這裡觀看旋轉模型) | ||||
| 類別 | 星形正多面體 星形十二面體 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 對偶多面體 | 大二十面體 | |||
| 識別 | ||||
| 名稱 | 大星形十二面體 | |||
| 參考索引 | U52, C68, W22 | |||
| 鮑爾斯縮寫 | gissid | |||
| 數學表示法 | ||||
| 考克斯特符號 | ||||
| 施萊夫利符號 | {5/2,3} | |||
| 威佐夫符號 | 3 | 2 5/2 | |||
| 性質 | ||||
| 面 | 12 | |||
| 邊 | 30 | |||
| 頂點 | 20 | |||
| 歐拉特徵數 | F=12, E=30, V=20 (χ=2) | |||
| 虧格 | 0 | |||
| 組成與佈局 | ||||
| 面的種類 | 12個五角星 | |||
| 面的佈局 | 12{5/2} | |||
| 頂點圖 | (5/2)3 | |||
| 對稱性 | ||||
| 對稱群 | Ih, H3, [5,3], (*532) | |||
| 特性 | ||||
| 正、非凸 | ||||
| 圖像 | ||||
| ||||
在幾何學上,大星形十二面體是一個由五角星組成的非凸正多面體[1],是正十二面體的星形多面體,其在非凸均勻多面體被編號為U52、在溫尼爾多面體模型被編號為W22。该多面體最早是由温佐·雅姆尼策尔於1568年發現並描述[2][3][4]。後來在1619年時,被約翰尼斯·克卜勒重新發現[5][6][7]。
大星形十二面體的對偶多面體也是一種星形正多面體,同時也是星形二十面體,其為由正三角形構成的大二十面體。
性質
[编辑]大星形十二面體共有12個面、30條邊和20個頂點[8],其每個面都是全等的正五角星[9]、每個頂點都是3個五角星的公共頂點,在頂點圖為三角形,可以用(5/2)3來表示[10],施萊夫利符號中利用 {5/2,3} 來表示,考克斯特符號中利用![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 來表示。
來表示。
二面角
[编辑]大星形十二面體是一種星形正多面體,因此具有所有角相等的性質。其二面角只有一个值,其值為五平方根倒數之反餘弦[11]:
頂點坐標
[编辑]邊長為單位長且幾何中心位於原點的大星形十二面體,其頂點坐標為[12]:
- 、
- 、
- 、
- 。
作為一個簡單多面體
[编辑]簡單多面體是指這個多面體中的面不會與同一個多面體的另一個面相交的多面體。若大星形十二面體要成為一個簡單多面體,則需要在這多面體中相交的面上放置新的頂點和邊,並將原本的五角星面分割成5個三角形面。這樣的多面體共有60個面、90條邊和32個頂點[13]
相關多面體
[编辑]| 名稱 | 大星形十二面體 | 截角大星形十二面體 | 大截半二十面体 | 截角大二十面體 | 大二十面體 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 考式 | |||||
| 圖像 | 
|

|

|

|

|
對偶複合體
[编辑]大二十面體與其對偶的複合體為複合大二十面體大星形十二面體。其共有32個面、60條邊和32個頂點,其尤拉示性數為4,虧格為-1,有12個非凸面[14],是一種截半二十面體的星形多面體[15][16]。溫尼爾在他的書中列出將這種形狀編為W61[17][18]。
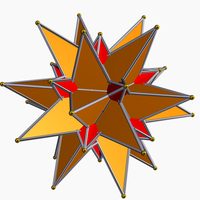
|
 從三角形的星狀圖 |
 從五邊形的星狀圖 |
參見
[编辑]參考文獻
[编辑]- Cauchy, A. L. "Recherches sur les polyèdres." J. de l'École Polytechnique 9, 68-86, 1813.
- ^ Coxeter, Star polytopes and the Schläfli function f(α,β,γ) p. 121 1. The Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. (编). 大星形十二面體. at MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. Wolfram Research, Inc. (英语).
- ^ Perspectiva corporum regularium. mathe.tu-freiberg.de. [2017-03-24]. (原始内容存档于2016-10-13).
- ^ Geometric Model by A. Harry Wheeler, Great Stellated Dodecahedron. americanhistory.si.edu. [2017-03-24]. (原始内容存档于2017-03-25).
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. (编). Kepler–Poinsot solid. at MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. Wolfram Research, Inc. (英语).
- ^ Johannes Kepler, Harmonices Mundi (1619).
- ^ Johannes Kepler with E. J. Aiton, A. M. Duncan, and J. V. Field, translators, The Harmony of the World, American Philosophical Society (1997).
- ^ great stellated dodecahedron. bulatov.org. [2016-09-02]. (原始内容存档于2016-03-26).
- ^ Great Stellated Dodecahedron. coolmath. [2016-09-02]. (原始内容存档于2016-08-26).
- ^ Cundy, H. and Rollett, A. "Great Stellated Dodecahedron. (5/2)3." §3.6.3 in Mathematical Models, 3rd ed. Stradbroke, England: Tarquin Pub., pp. 94-95, 1989.
- ^ Kepler-Poinsot Solids: Great Stellated Dodecahedron. dmccooey.com. [2016-09-02]. (原始内容存档于2016-03-24).
- ^ Data of Great Stellated Dodecahedron. dmccooey.com. [2016-10-01]. (原始内容存档于2016-10-01).
- ^ Alexander Bogomolny. Great Stellated Dodecahedron. cut-the-knot.org. [2016-09-02]. (原始内容存档于2016-08-26).
- ^ compound of great stellated dodecahedron and great icosahedron. bulatov.org. [2016-09-02]. (原始内容存档于2015-09-06).
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. (编). Great Icosahedron-Great Stellated Dodecahedron Compound. at MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. Wolfram Research, Inc. (英语).
- ^ H. Cundy and A. Rollett Great Icosahedron Plus Great Stellated Dodecahedron. §3.10.4 in Mathematical Models, 3rd ed. Stradbroke, England: Tarquin Pub., pp. 132-133, 1989.
- ^ Wenninger, Magnus. Polyhedron Models. Cambridge University Press. 1974. ISBN 0-521-09859-9.
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. (编). Great Icosahedron-Great Stellated Dodecahedron Compound. at MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. Wolfram Research, Inc. (英语).








