File:Titan-SaturnMoon-Maps-TraceGases-20141022.jpg

原始文件 (846 × 424像素,文件大小:87 KB,MIME类型:image/jpeg)
摘要
| 描述Titan-SaturnMoon-Maps-TraceGases-20141022.jpg |
English: October 22, 2014
RELEASE 14-037 http://www.nasa.gov/press/goddard/2014/october/nasa-led-study-sees-titan-glowing-at-dusk-and-dawn/ IMAGE: DESCRIPTION: The pair of patches was spotted by a NASA-led international team of researchers investigating the chemical make-up of Titan’s atmosphere. “This is an unexpected and potentially groundbreaking discovery,” said Martin Cordiner, an astrochemist working at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and the lead author of the study. “These kinds of east-to-west variations have never been seen before in Titan’s atmospheric gases. Explaining their origin presents us with a fascinating new problem.” The mapping comes from observations made by the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), a network of high-precision antennas in Chile. At the wavelengths used by these antennas, the gas-rich areas in Titan’s atmosphere glowed brightly. And because of ALMA’s sensitivity, the researchers were able to obtain spatial maps of chemicals in Titan’s atmosphere from a “snapshot” observation that lasted less than three minutes. Titan’s atmosphere has long been of interest because it acts as a chemical factory, using energy from the sun and Saturn’s magnetic field to produce a wide range of organic, or carbon-based, molecules. Studying this complex chemistry may provide insights into the properties of Earth’s very early atmosphere, which may have shared many chemical characteristics with present-day Titan. In this study, the researchers focused on two organic molecules, hydrogen isocyanide (HNC) and cyanoacetylene (HC3N), that are formed in Titan’s atmosphere. At lower altitudes, the HC3N appears concentrated above Titan’s north and south poles. These findings are consistent with observations made by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, which has found a cloud cap and high concentrations of some gases over whichever pole is experiencing winter on Titan. The surprise came when the researchers compared the gas concentrations at different levels in the atmosphere. At the highest altitudes, the gas pockets appeared to be shifted away from the poles. These off-pole locations are unexpected because the fast-moving winds in Titan’s middle atmosphere move in an east–west direction, forming zones similar to Jupiter’s bands, though much less pronounced. Within each zone, the atmospheric gases should, for the most part, be thoroughly mixed. The researchers do not have an obvious explanation for these findings yet. “It seems incredible that chemical mechanisms could be operating on rapid enough timescales to cause enhanced 'pockets' in the observed molecules,” said Conor Nixon, a planetary scientist at Goddard and a coauthor of the paper, published online today in the Astrophysical Journal Letters. “We would expect the molecules to be quickly mixed around the globe by Titan’s winds.” At the moment, the scientists are considering a number of potential explanations, including thermal effects, previously unknown patterns of atmospheric circulation, or the influence of Saturn’s powerful magnetic field, which extends far enough to engulf Titan. Further observations are expected to improve the understanding of the atmosphere and ongoing processes on Titan and other objects throughout the solar system. NASA’s Astrobiology Program supported this work through a grant to the Goddard Center for Astrobiology, a part of the NASA Astrobiology Institute. Additional funding came from NASA’s Planetary Atmospheres and Planetary Astronomy programs. ALMA, an international astronomy facility, is funded in Europe by the European Southern Observatory, in North America by the U.S. National Science Foundation in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada and the National Science Council of Taiwan, and in East Asia by the National Institutes of Natural Sciences of Japan in cooperation with the Academia Sinica in Taiwan. Nancy Neal-Jones / Elizabeth Zubritsky NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. 301-286-0039 / 301-614-5438 [email protected] / [email protected] |
| 日期 | |
| 来源 | http://www.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/thumbnails/image/titanmoleculesimage.jpg |
| 作者 | NRAO/AUI/NSF |
| 授权 (二次使用本文件) |
https://public.nrao.edu/mediause |
许可协议
| All images and videos released by NRAO on their website are copyright protected on behalf of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI), and the National Science Foundation (NSF), and are licensed for use under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/) in accordance with the conditions below. See the NRAO Image Use Policy for complete information.
Conditions:
Notes:
|
 |
- 您可以自由地:
- 共享 – 复制、发行并传播本作品
- 修改 – 改编作品
- 惟须遵守下列条件:
- 署名 – 您必须对作品进行署名,提供授权条款的链接,并说明是否对原始内容进行了更改。您可以用任何合理的方式来署名,但不得以任何方式表明许可人认可您或您的使用。
说明
此文件中描述的项目
描绘内容
知识共享署名3.0未本地化版本 简体中文(已转写)
22 10 2014
文件历史
点击某个日期/时间查看对应时刻的文件。
| 日期/时间 | 缩略图 | 大小 | 用户 | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 当前 | 2014年10月23日 (四) 12:50 | 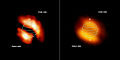 | 846 × 424(87 KB) | Drbogdan | User created page with UploadWizard |
文件用途
全域文件用途
以下其他wiki使用此文件:
- af.wikipedia.org上的用途
- an.wikipedia.org上的用途
- ar.wikipedia.org上的用途
- azb.wikipedia.org上的用途
- cs.wikipedia.org上的用途
- el.wikipedia.org上的用途
- en.wikipedia.org上的用途
- en.wikiversity.org上的用途
- hy.wikipedia.org上的用途
- id.wikipedia.org上的用途
- ja.wikipedia.org上的用途
- ko.wikipedia.org上的用途
- mk.wikipedia.org上的用途
- pt.wikipedia.org上的用途
- uk.wikipedia.org上的用途
元数据
此文件中包含有扩展的信息。这些信息可能是由数码相机或扫描仪在创建或数字化过程中所添加。
如果此文件的源文件已经被修改,一些信息在修改后的文件中将不能完全反映出来。
| 方向 | 正常 |
|---|---|
| 水平分辨率 | 72 dpi |
| 垂直分辨率 | 72 dpi |
| 使用软件 | Adobe Photoshop CS6 (Windows) |
| 文件修改日期时间 | 2014年10月22日 (三) 10:43 |
| 色彩空间 | sRGB |
| 数字化日期时间 | 2014年10月22日 (三) 06:41 |
| 元数据最后修改日期 | 2014年10月22日 (三) 06:43 |
| 原始文件唯一ID | xmp.did:89875F94F959E4118276CB85C8F3B5EA |


